
One set of blood vessels circulates blood through the lungs. Use this coloring page for notebooking pages, or science displays. This is a simple illustration of the human heart for children to color, label, or draw direction of blood flow. Featuring six of the basic parts of the heart, each numbered and labeled for easy identification.
#Heart blood flow diagram free
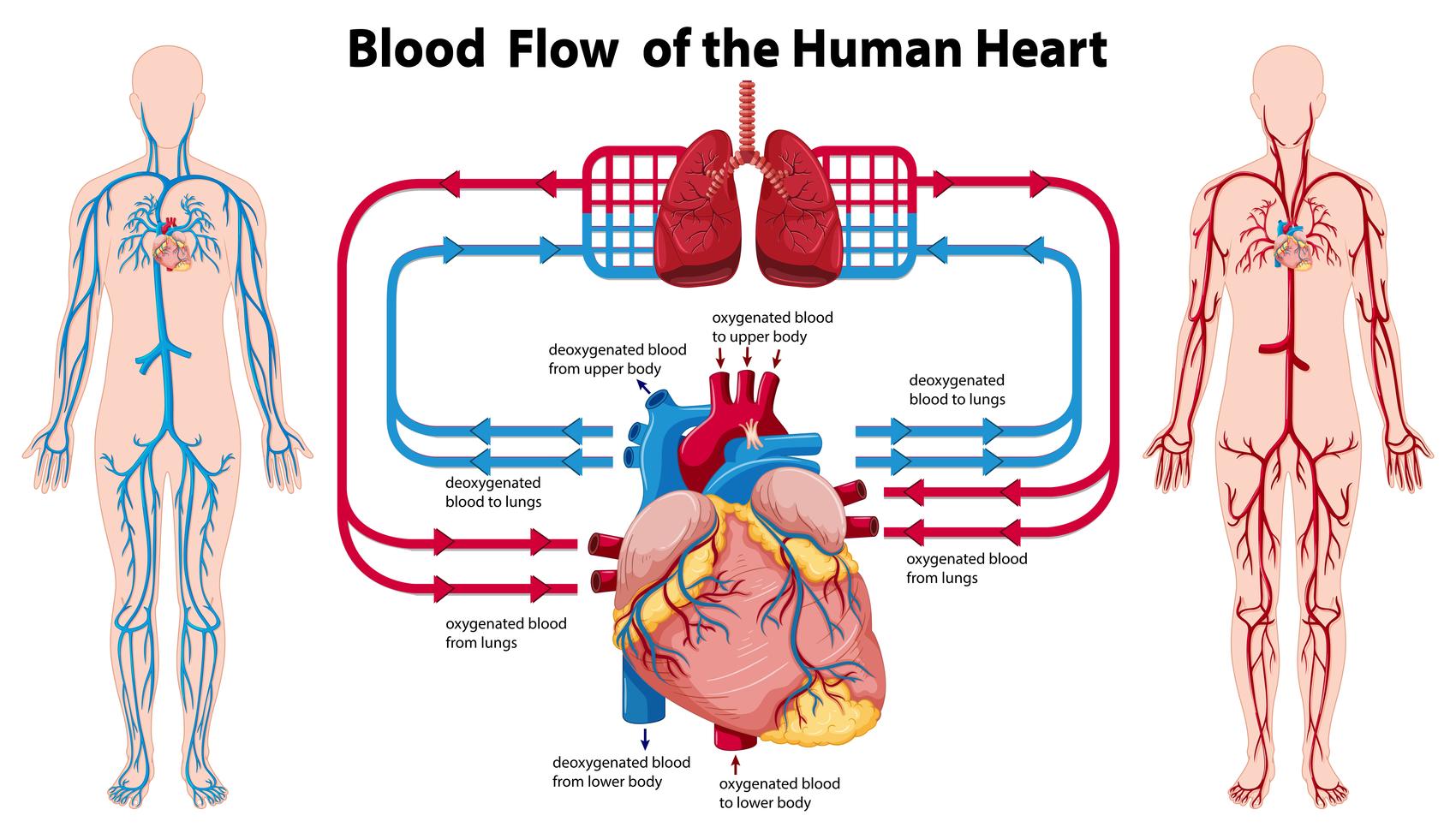
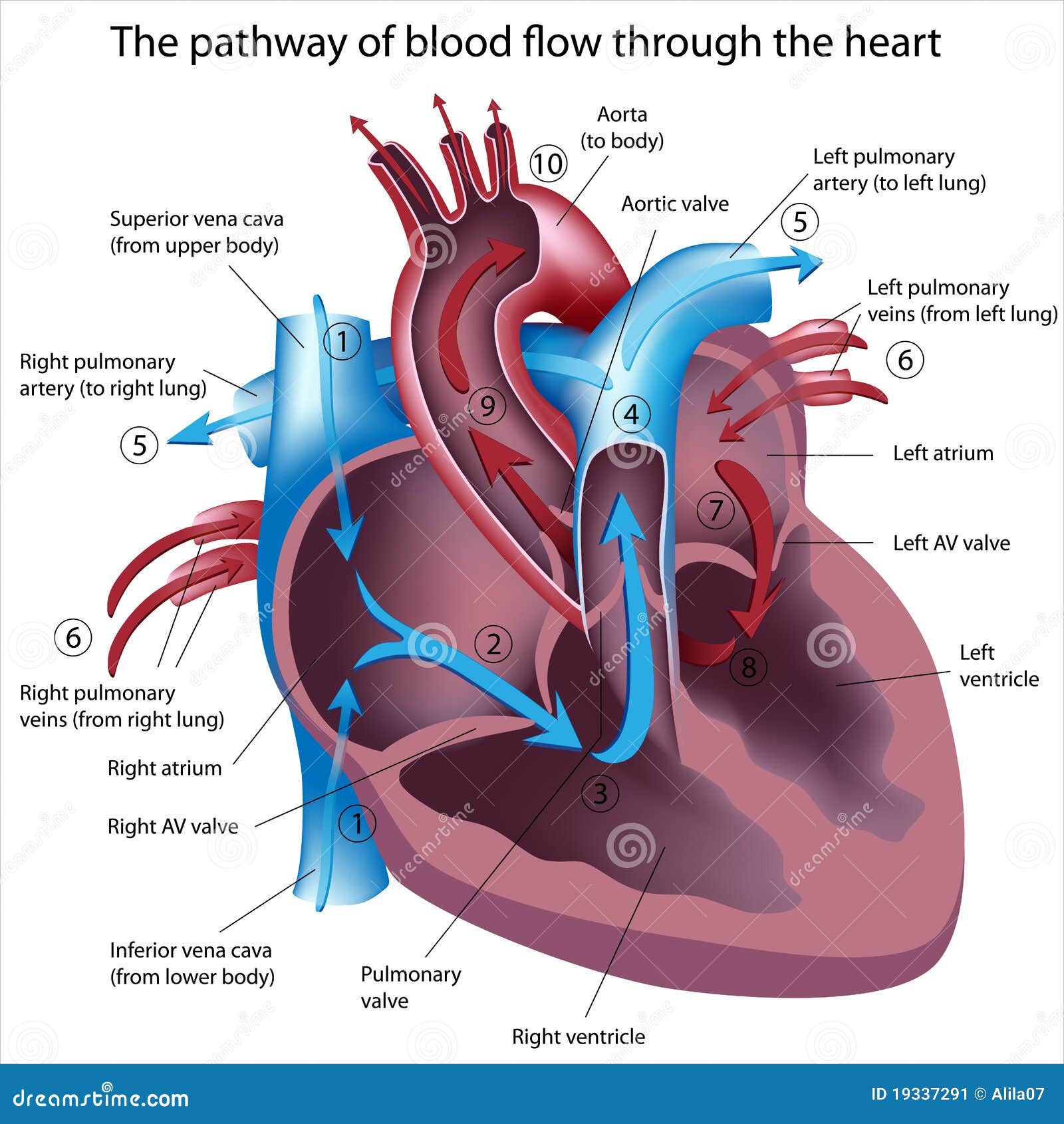
These are the first arteries to branch off from the aorta. The pumping of the heart drives this blood flow through the arteries, capillaries, and veins. This is a simple and free human heart anatomy chart for kids. The heart muscle cells are supplied with blood by the coronary arteries. The heart contains valves to prevent the backflow of blood. The blood is oxygenated in the lungs and flows back to the heart in the pulmonary vein, into the left atrium and down into the left ventricle where it is pushed up and out of the aorta to the body. Origin to destination of blood it carriesĭeoxygenated blood coming from the body flows through the vena cava into the right atrium and down into the right ventricle where it is pumped to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Blood is carried away from the heart in the pulmonary artery and the aorta when the ventricles contract. The vena cava and pulmonary vein carry blood into the heart. The mammalian heart contains four chambers connected to four major blood vessels. Your circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients to your heart and the other cells of your body. This means that a red blood cell will travel through the heart twice during a complete circulation around the body. Your blood also carries oxygen inhaled by the lungs. The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs and the left side pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body tissues. Blood is pumped away from the heart in arteries ('a' for away) and is returned to the heart in veins. After collecting in the left atrium it passes into the left ventricle and from there is pumped to the body by way of the aorta.Blood is pumped around the body of a vertebrate by the heart. Cardiac output (Q) is distributed to respiratory circulation via afferent. Red blood (blood with oxygen) returns back from the lungs by way of the pulmonary veins. Differences in blood pressures in fish lineages.

In the lungs, the blood collects oxygen and turns a red color. The right ventricle then pumps the blue blood out to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. After collecting in the right atrium, it passes to the right ventricle. Normally blue blood (blood without oxygen) returns from the upper portion of the body by way of the superior vena cava and from the lower portion of the body by way of the inferior vena cava. The job of the heart is to pump blood to both the heart and the body. The pulmonary artery connects the right ventricle to the lungs, while the aorta connects the left ventricle to the body. The superior and inferior vena connect to the right atrium, while the pulmonary veins connect to the left atrium. Finally, there are a number of veins and arteries attaching to the heart. The valves open to allow blood to flow forward and close to prevent any backflow. There are four separate valves in the heart: the tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and aortic valve. The wall dividing the two ventricles is called the ventricular septum. The ventricles are muscular chambers responsible for pumping blood to the body and lungs. Four valves regulate blood flow through your heart: The tricuspid valve regulates blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle. The lower two chambers are the right and left ventricles (RV and LV).

On the evolutionary cycle, pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians, the first animals to acquire a three-chambered heart. The wall dividing the two atria is called the atrial septum. pulmonary circulation, system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs, as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues. The atria are the receiving chambers for blood returning from the body and the lungs. The upper two chambers are called the right and left atria (RA and LA).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
